Please find earlier blogs to have understanding of our Data Engineering Learning plan and system setup for Data Engineering. Today we are solving and learning one more Data engineering problem and learning new concepts.
Problem Statement
Query the two cities in STATION with the shortest and longest CITY names, as well as their respective lengths (i.e.: number of characters in the name). If there is more than one smallest or largest city, choose the one that comes first when ordered alphabetically. The STATION table is described as follows:
Problem Difficulty Level: Hard
Data Structure
- ID
- City
- State
- Lattitude
- Longitude

Data for station table
Sample Input
For example, CITY has four entries: DEF, ABC, PQRS and WXY.
Sample Output:
ABC 3
PQRS 4Please clone below GitHub repo in which we have all the data and problem solution with PostgreSQL, Apache Spark and Spark SQL.
https://github.com/developershomes/DataEngineeringProblems/tree/main/Problem%204
Solve using SQL (PostgreSQL)
First create tables into PostgreSQL using create script and also import data into tables as we discussed in earlier blogs. And list both tables’ data so we have understanding of data.
Once data is loaded in table, we will do select query to check data,
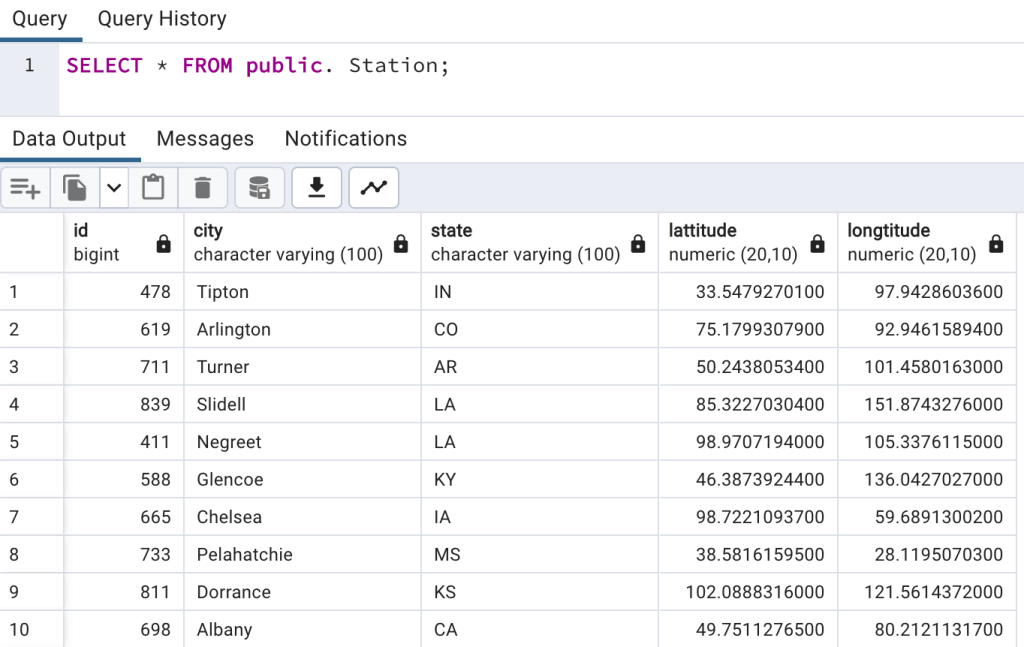
As usual, we will divide this problem into multiple steps.
- We need shortest and longest City names with its length
- So first we will get length of all cities
- Also, if in case we have same length of character in shortest we want to order by alphabetically and give rank to city.
- After that we will get what is shortest length of city and what is longest length of city
- After that we will filter those two cities with the longest and shortest length and also order by alphabetically.
First step, we will get length of each city. For that we will use length function in SQL.
SELECT city, length(city) FROM public. Station;
On the next step, if we have two cities with the same length, we will give priority based on alphabatically. In other words, we will give rank to same length city order by alphabatically.
Here, we will use windows function RANK() , we will give rank to cities. We also want to give rank to cities whose having same length. So, we also need to use PARTITION BY and we want to order by name of city hence we will also use ORDER BY. So our query will be as below.
SELECT CITY
,LENGTH(CITY) as citylength
,RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY LENGTH(CITY) ORDER BY LENGTH(CITY),CITY) as actualrank
FROM STATION;
We can see that with length 3, we have two cities, Amo and Roy. And It gave rank Amo as 1 and Roy as 2.
So now if in case we only prioritize the first city in each length, we can simply say that we only want city with actualrank = 1.
On next step, we will get min and max length of cities from all cities.
For that we will use MIN() and MAX() functions in SQL. So, our query will be as below.
SELECT MIN(LENGTH(CITY)) as minimumLength,MAX(LENGTH(CITY)) as maximumLength FROM STATION;

Now, Final part where we will merge all of above queries.
First, we will filter all the cities with rank 1 (in our case we have given name as actualrank).
SELECT q1.city, q1.citylength
FROM
(SELECT CITY,LENGTH(CITY) as citylength, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY LENGTH(CITY) ORDER BY LENGTH(CITY),CITY) as actualrank
FROM STATION) q1
WHERE q1. actualrank = 1 ;
Next step, filter with minimum and maximum length.
SELECT q1.city, q1.citylength
FROM
(SELECT CITY,LENGTH(CITY) as citylength, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY LENGTH(CITY) ORDER BY LENGTH(CITY),CITY) as actualrank
FROM STATION) q1
WHERE q1. actualrank = 1
AND q1.citylength = (SELECT MIN(LENGTH(CITY)) FROM STATION)
OR q1.citylength = (SELECT MAX(LENGTH(CITY)) FROM STATION);
This is how we solved this complex problem by diving this problem in small steps.
Solve Problem using Spark
In Spark, we will solve this problem using PySpark functions and also using Spark SQL.
First for both, we need to load data into Dataframe. First open Jupyter Lab and create one file and paste CSV data into that file.
Now, create Jupyter notebook using python as engine (kernel).
We have already loaded data into dataframe.
Now we check schema so we are sure that all the columns have proper datatypes.

Also check data

Solve using Spark SQL
Before using Spark SQL, we need to create a temp table (or HIVE table) from data frame.

We have already solved this problem using PostgreSQL earlier and we know that Spark SQL is always works with almost all ANSI SQL functions. So, we will direct use that query by changing table name with temp table.
We have same LENGTH(), RANK() , MIN() and MAX() functions available in Spark SQL.
# Now we will write query to get max salary for each employee
# so we will use SQL Group by and SQL Order by functions
sqlContext.sql("SELECT q1.city, q1.citylength FROM \
(SELECT CITY,LENGTH(CITY) as citylength, RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY LENGTH(CITY) ORDER BY LENGTH(CITY),CITY) as actualrank \
FROM tmpStation) q1 \
WHERE q1. actualrank = 1 \
AND q1.citylength = (SELECT MIN(LENGTH(CITY)) FROM tmpStation) \
OR q1.citylength = (SELECT MAX(LENGTH(CITY)) FROM tmpStation)").show(n=100)

Conclusion
Today, we learn very important and most used SQL Functions
LENGTH() -> To get length of String
MIN() -> Get minimum value from column
MAX() -> Get maximum value from column
RANK() -> Rank will be used to get rank in table. We have to pass PARTITION BY with rank function. And ORDER BY can be passed to get rank based on columns ascending or descending order.
Please also find the video to understand this problem in more detail. And also follow this blog to learn more.
Part 1 (Using PostgreSQL)
Using Apache Spark (Spark SQL)
Leave a comment