Please find earlier blogs to have understanding of our Data Engineering Learning plan and system setup for Data Engineering. Today we are solving and learning one more Data Engineering problem and learning new concepts. For earlier problem solution and key learning points follow below.
https://developershome.blog/category/data-engineering/problem-solving/
Problem Statement
Query the list of CITY names starting with vowels (i.e., A, E, I, O, or U) from STATION. Your result cannot contain duplicates. The STATION table is described as follows:
Problem Difficulty Level: Easy
Data Structure
- ID
- City
- State
- Lattitude
- Longitude

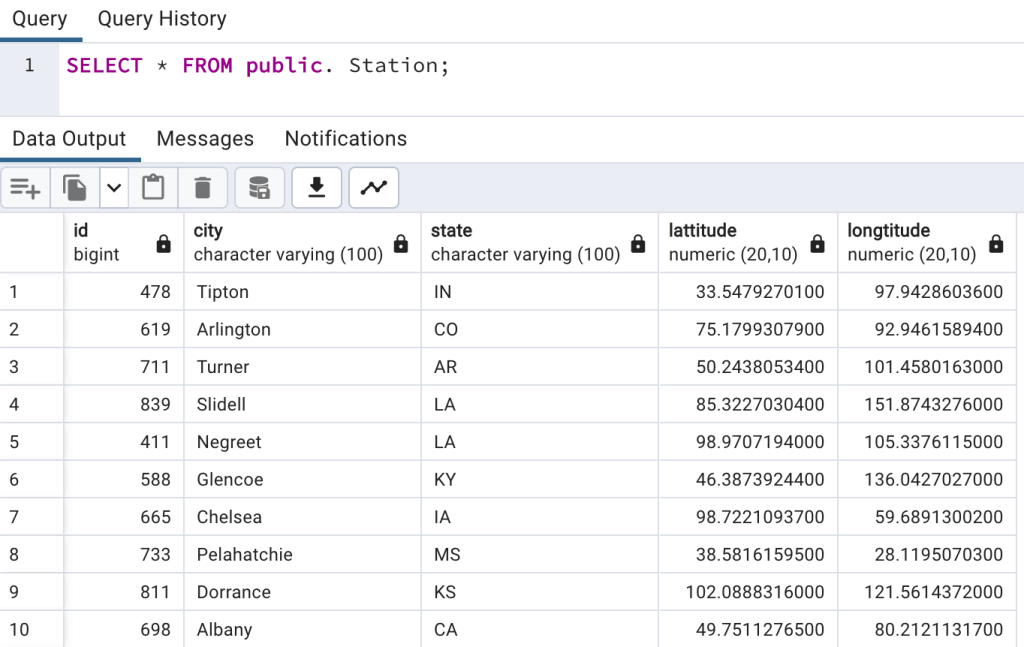
Data for station table
Please clone below GitHub repo in which we have all the data and problem solution with PostgreSQL, Apache Spark and Spark SQL.
https://github.com/developershomes/DataEngineeringProblems/tree/main/Problem%205
Solve using SQL (PostgreSQL)
First create tables into PostgreSQL using create script and also import data into tables as we discussed in earlier blogs. And list both tables’ data so we have understanding of data.
Once data is loaded in table, we will do select query to check data,
As usual, we will divide this problem into multiple steps.
- First, we will get first character of city
- And filter that with vowels
- And we will also use distinct functions so that we will not have duplicate cities.
In SQL, we have LEFT() and RIGHT(). With those functions we need to pass how many left or right characters are required. Here we need first character so we will pass left(String,1)
SELECT CITY, LEFT(CITY,1) FROM STATION;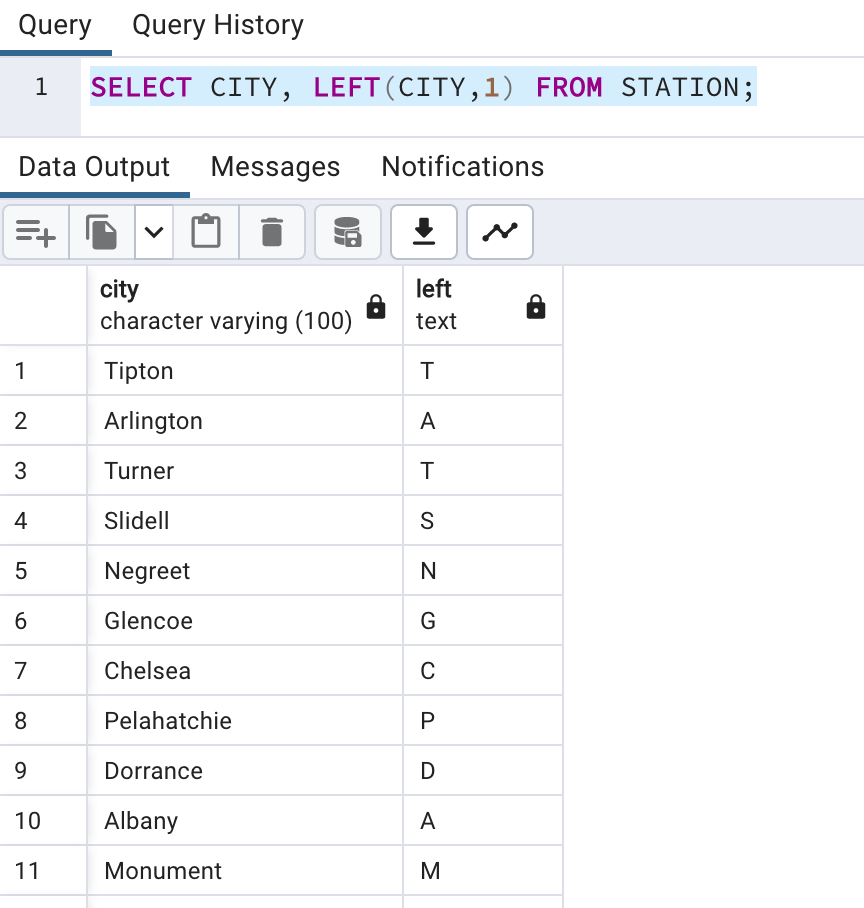
Now, we will use filter condition and also use distinct city so that we will not have duplicates city names in output.
SELECT DISTINCT(CITY) FROM STATION WHERE LEFT(CITY,1) IN ('A','E','I','O','U');
This is how we solved this problem.
Solve Problem using Spark
In Spark, we will solve this problem using PySpark functions and also using Spark SQL.
First for both, we need to load data into Dataframe. First open Jupyter Lab and create one file and paste CSV data into that file.
Now, create Jupyter notebook using python as engine (kernel).
We have already loaded data into dataframe.
Now we check schema so we are sure that all the columns have proper datatypes.

Also check data

Solve using PySpark functions
In PySpark, we have the same LEFT() function available. We will use the same function and apply filter condition on dataframe.
#Solving Problem using PySpark
# ind the difference between the total number of CITY entries in the table and the number of distinct CITY entries in the table.
stationdf.select("City").where("Left(City,1) IN ('A','E','I','O','U')").show(n=100)
Solve using Spark SQL
Before using Spark SQL, we need to create a temp table (or HIVE table) from data frame.

We have already solved this problem using PostgreSQL earlier and we know that Spark SQL is always works with almost all ANSI SQL functions. So we will direct use that query by changing table name with temp table.
# Now we will write query to get max salary for each employee
# so we will use SQL Group by and SQL Order by functions
sqlContext.sql("SELECT DISTINCT(CITY) FROM tmpStation WHERE LEFT(CITY,1) IN ('A','E','I','O','U')").show(n=100)
Conclusion:
Today, we have learned below SQL functions
LEFT() -> To get left character/characters from string
RIGHT() -> To get right character/characters from string
DISTINCT() -> Get unique values from column
IN -> when we want to pass multiple filter condition, we use IN.
Please also find the video to understand this problem in more detail. And also follow this blog to learn more.
Leave a comment