Previous blog/Context:
In an earlier blog, we discussed Spark ETL with files (CSV, JSON, Text, Paraquet and ORC). Please find below blog post for more details.
Introduction:
In this blog post, we will discuss Spark ETL with SQL Database. We will be considering MySQL and PostgreSQL for Spark ETL. All other SQL Databases like MS SQL, RedShift and Oracle, they also follow same pattern, only difference is we need to download different Maven package for different database. We will also discuss how to select and specify Maven packages for any database.

Today, we will be doing below Spark ETL
Task to do
1. Install required spark libraries (MySQL & PostgreSQL)
2. Create connection with SQL Database (MySQL & PostgreSQL)
3. Read data from SQL Database (MySQL & PostgreSQL)
4. Transform data
5. write data into SQL Server (MySQL & PostgreSQL)
First clone below GitHub repo, where we have all the required sample files and solution.
https://github.com/developershomes/SparkETL/tree/main/Chapter1
If you don’t have setup for Spark instance, MySQL or PostgreSQL in your system follow earlier blog for setting up Data Engineering tools in your system. (Data Engineering suite will setup Spark, MySQL, PostgreSQL and MongoDB in your system)
Spark ETL with SQL Database
First open Jupyter Notebook and copy all the content of Chapter 1 from GitHub to there.
First, we will do all the ETL with MySQL and after that we will do it with PostgreSQL.
With our Spark Instance, we have a few spark libraries that are already installed but before doing MySQL or PostgreSQL we need to check that do we have libraries for that is already installed or not.
From docker desktop, go to terminal of Spark container or use docker exec -it
Now, go to directory /opt/spark/jars

Now, go to Jars folder and list all the Jar files

Here, we see that with our spark instance, we have all the libraries/packages installed for ADLS/blob, S3, GCP, Delta, Avro and Snowflake. But we don’t have packages installed for MySQL or PostgreSQL.
Spark ETL with MySQL
First with starting Spark session, we will also download and install MySQL Packages from Maven. You can check all the packages from Maven using this link
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/mysql/mysql-connector-java
For downloading and installing any packages, we need to use below config
'spark.jars.packages':'mysql:mysql-connector-java:8.0.32'So, our code for starting Spark session will be as below
#Start Spark Session
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("chapter1")\
.config('spark.jars.packages', 'mysql:mysql-connector-java:8.0.32')\
.getOrCreate()
sqlContext = SparkSession(spark)
#Dont Show warning only error
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("ERROR")It will first download package from Maven and then install it
Now, we have required library installed for MySQL so we can do Spark ETL with MySQL.
Create connection with MySQL Database & Read Data from Table
We have MySQL Database with the name DATAENG and in that database we already have table with name user is there, we will read that table from Spark. (If you don’t have table created with data use CSV file from GitHub and create and load data into MySQL)
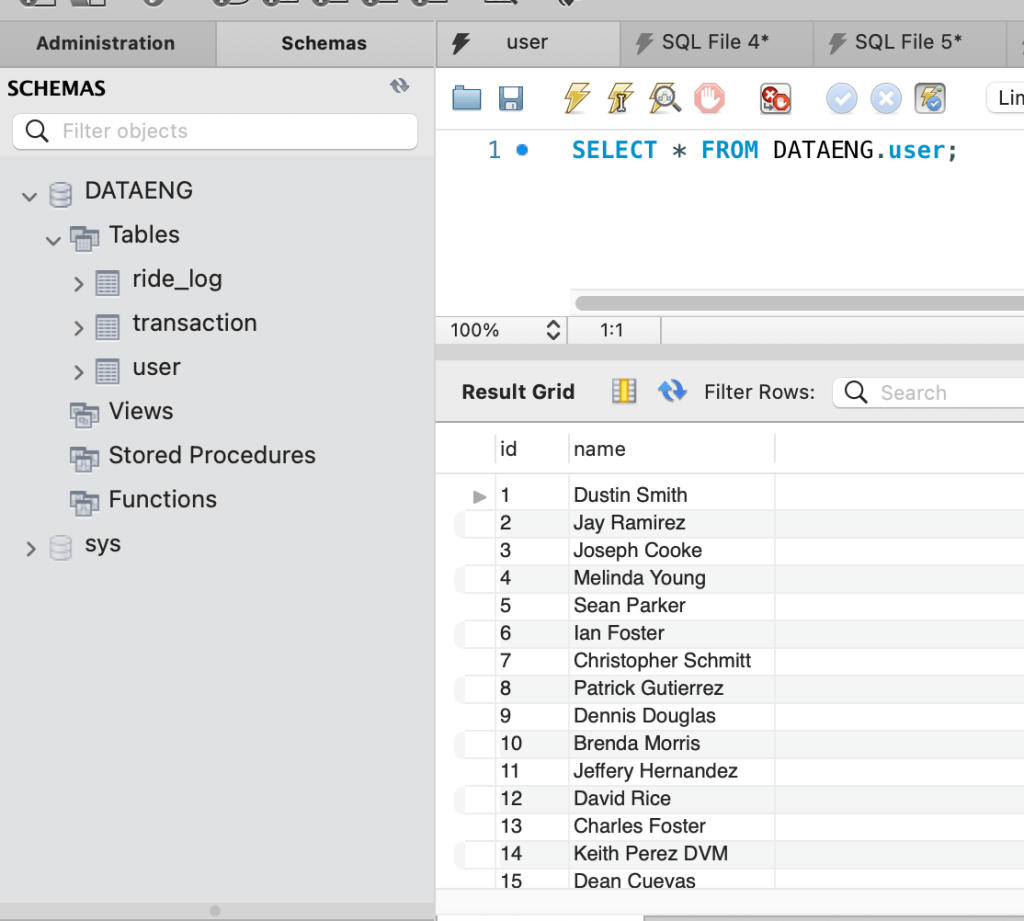
Spark code for creating connection with MySQL and reading table will be as below
#Load CSV file into DataFrame
mysqldf = spark.read \
.format("jdbc") \
.option("driver","com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver") \
.option("url", "jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.104:3306/DATAENG") \
.option("dbtable", "user") \
.option("user", "root") \
.option("password", "mysql") \
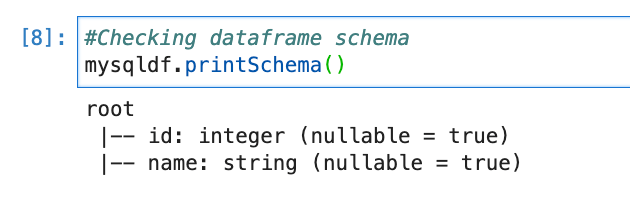
.load()#Checking dataframe schema
mysqldf.printSchema()In URL, we need to pass MySQL database location. We have database running on localhost only so we should have used 127.0.0.1 but our spark will connect that from inside docker so it will consider docker’s 127.0.0.1 and that’s why in our scenario (with this setup) we need to pass our local assigned IP address.
Once connection is done, we will check schema and data into that dataframe
mysqldf.show(n=10)
We will create Temp table (or HIVE view) so that we can write Spark SQL for transformation.
mysqldf.createOrReplaceTempView("tempMySQL")Transform data
sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM tempMySQL").show(n=5)
For transformation, we will filter users who is having id more than 40 and store into other dataframe.
newdf = sqlContext.sql("SELECT name as fullname FROM tempMySQL WHERE id > 40")
newdf.count()
Write data to MySQL
Using the command below, we will write to MySQL. We will ask to create a table and load data into a table from dataframe.
newdf.write \
.format("jdbc") \
.option("driver","com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver") \
.option("url", "jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.104:3306/DATAENG") \
.option("dbtable", "username") \
.option("user", "root") \
.option("password", "mysql") \
.save()Now, if we go to MySQL and check, we will see table with same data.

Spark ETL with PostgreSQL
We don’t have PostgreSQL package/library installed in our Spark instance. So, we need to install Spark package for PostgreSQL also.
We will use the Spark PostgreSQL package from Maven.
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.postgresql/postgresql
Code for starting Spark session with specifying Spark Package
#Start Spark Session
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("chapter1PostgreSQL")\
.config('spark.jars.packages', 'org.postgresql:postgresql:42.5.4')\
.getOrCreate()
sqlContext = SparkSession(spark)
#Dont Show warning only error
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("ERROR")This will first download PostgreSQL package and install it.
We have PostgreSQL packages installed so now we can do all the ETL operation with PostgreSQL.
Create connection and Read data from PostgreSQL from Spark
We have created employee (employee salary) table in PostgreSQL server for solving data engineering problems, we will read that table from Spark. (If you don’t have table and data in PostgreSQL, use provided CSV file and import into PostgreSQL)

Code for the same
postgredf = spark.read.format("jdbc") \
.option("url", "jdbc:postgresql://192.168.1.104:5432/postgres") \
.option("driver", "org.postgresql.Driver") \
.option("dbtable", "public.employee_salary") \
.option("user", "postgres") \
.option("password", "postgres")\
.load()
postgredf.printSchema()
postgredf.show(n=10)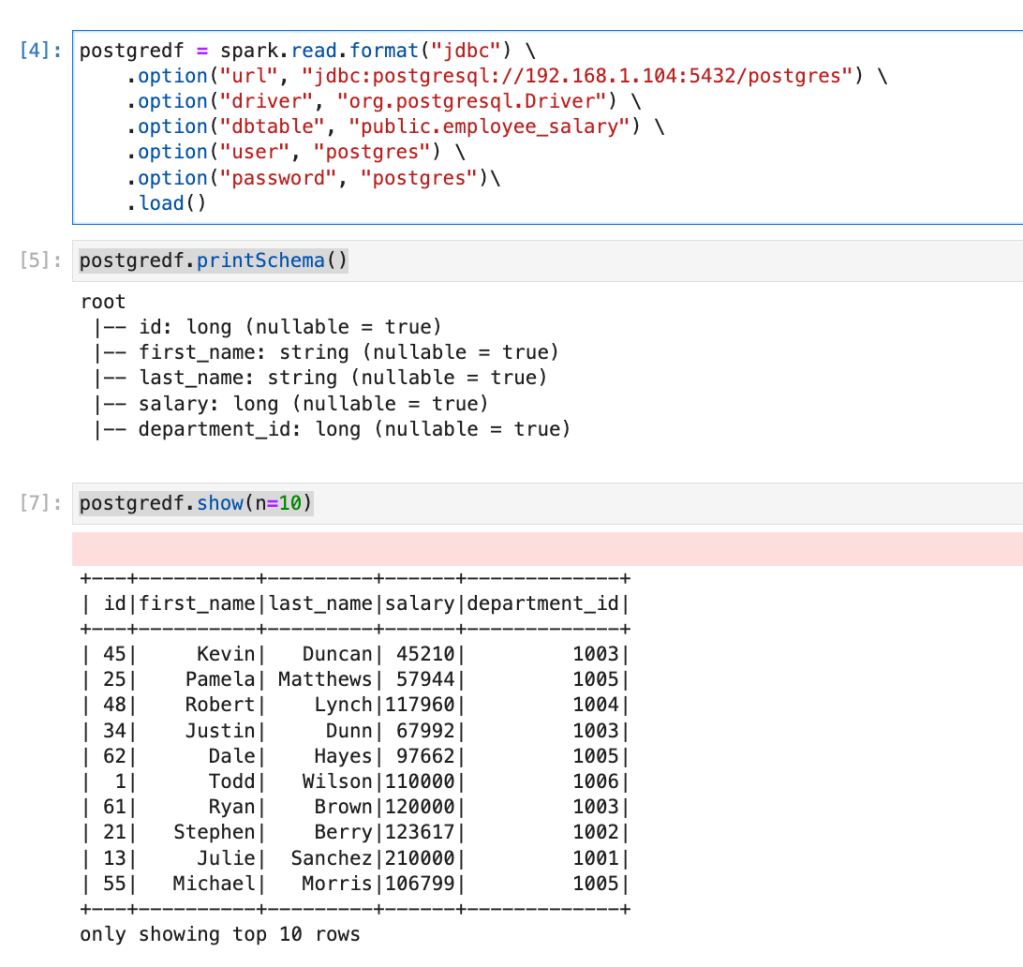
We have data from PostgreSQL available into dataframe, we will create temp table (or HIVE view) so that we can do Spark SQL.
postgredf.createOrReplaceTempView("tempPostgreSQL")Transform data
We will filter employees with more than 50000 salary and store them into dataframe.
newdf = sqlContext.sql("SELECT first_name,salary FROM tempPostgreSQL WHERE salary > 50000")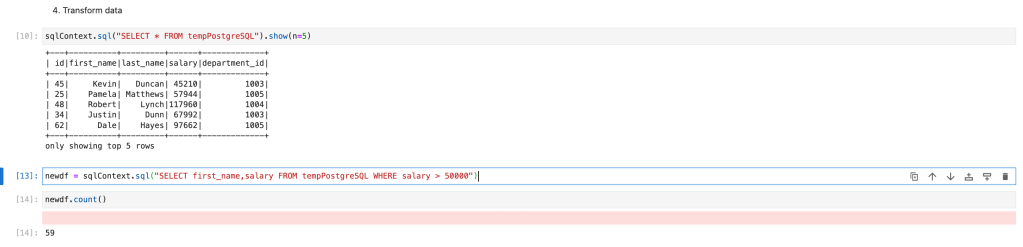
write data into PostgreSQL Server
We will store data from dataframe to PostgreSQL.
newdf.write \
.format("jdbc") \
.option("url", "jdbc:postgresql://192.168.1.104:5432/postgres") \
.option("driver", "org.postgresql.Driver") \
.option("dbtable", "public.employee1") \
.option("user", "postgres") \
.option("password", "postgres")\
.save()This will create a table in PostgreSQL (if a table is not already there) and load data into the table.
Conclusion:
We have learned how to install and download Spark Packages if it is not already there. We also learned below topics.
- How to create connection with MySQL and PostgreSQL
- How to read tables (views) from MySQL and PostgreSQL using spark. Read
- How to create Hive table (views) and do transformation
- How to load data into MySQL and PostgreSQL from Spark using spark. Write
- Here, we have observed that in both cases it first downloaded JDBC drivers and created connection using JDBC. (For read and write both)