Previous blog/Context:
In an earlier blog, we discussed Spark ETL with NoSQL Databases (MongoDB Database). Please find below blog post for more details.
Introduction:
In this blog, we will discuss Spark ETL with Cloud data lakes and we will be doing Spark ETL with Azure Blob storage. We will use public blob storage and we will understand how to do ETL with Azure Blob storage. In coming blogs, we will be also doing Spark ETL with AWS S3 bucket and Google buckets.
Today, we will perform below Spark ETL operations
- Install required spark libraries
- Create connection with Azure Blob storage
- Read data from blob and store into dataframe
- Transform data
- write data into parquet file
- write data into JSON file
First clone below GitHub repo, where we have all the required sample files and solution
https://github.com/developershomes/SparkETL/tree/main/Chapter3
If you don’t have setup for Spark instance follow earlier blog for setting up Data Engineering tools in your system. (Data Engineering suite will setup Spark, MySQL, PostgreSQL and MongoDB in your system) In that Spark instance we already have packages installed for Azure blog storage and Azure Data Lake Services.
Public Azure Blob Storage
We are going to access Public Azure blob storage from Spark. As a part of Azure Open Datasets, there are different types of data publicly available for learning purposes.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/open-datasets/dataset-catalog

We will be using NYC yellow taxi data.
Install required spark libraries & Start Spark Session
With our Spark instance, we already have Azure Blob storage and ADLS packages installed. So, we will not require to specify externally. You can check Jars files from /opt/spark/jars location

If you want to use the same package you can use the Maven repo link and pass it in the config file.
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.microsoft.azure/azure-storage/7.0.1
We will start our Spark session.
Create connection with Azure Blob storage from Spark
For connecting to Azure blob storage, we need the details below. Like what is account name, what is container name and what is key for connecting that storage and relative path. We have three different datasets
- NYC Yellow taxi data -> very high volume
- Covid public data -> Medium volume
- Public holidays -> low volume
Let’s start here with NYC yellow taxi data.
The volume of data is too high. 50 billion rows and 50 GB of data. (All in parquet format)
# Azure storage for NYC Yellow taxi
blob_account_name = "azureopendatastorage"
blob_container_name = "nyctlc"
blob_relative_path = "yellow"
blob_sas_token = "r"If you want to try Covid Public data you can use the blob details. (NYC taxi is very big data set so it will take time to load all data)
The volume of data is medium. 125 K rows and around 40 MB of parquet file.
# Azure storage for Covid dataset
blob_account_name = "pandemicdatalake"
blob_container_name = "public"
blob_relative_path = "curated/covid-19/bing_covid-19_data/latest/bing_covid-19_data.parquet"
blob_sas_token = r""If you want to try a very small data set, use the holiday list below which is 500KB of data and 70,000 rows.
# Azure storage for Holiday
blob_account_name = "azureopendatastorage"
blob_container_name = "holidaydatacontainer"
blob_relative_path = "Processed"
blob_sas_token = r""Once we declare variable for all of details. We will create connection string and set in Spark configuration as below. I am going ahead with yellow taxi data but I will suggest trying with public holiday. (As volume is low so it will do all the operations faster)
# Allow SPARK to read from Blob remotely
wasbs_path = 'wasbs://%s@%s.blob.core.windows.net/%s' % (blob_container_name, blob_account_name, blob_relative_path)
spark.conf.set(
'fs.azure.sas.%s.%s.blob.core.windows.net' % (blob_container_name, blob_account_name),
blob_sas_token)
print('Remote blob path: ' + wasbs_path)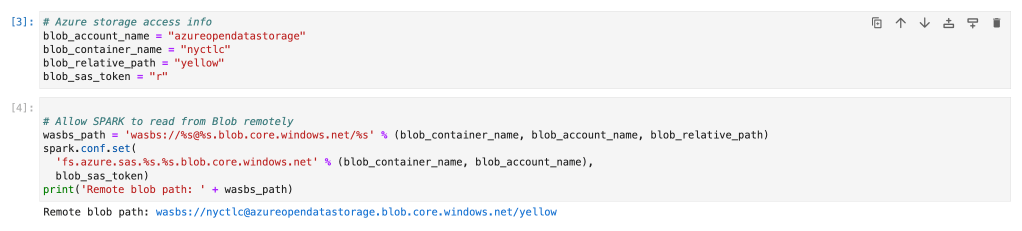
Read data from blob and store into dataframe
Next step is read data from this location. We have parquet files stored in location. So, we will use spark.read.parquet
df = spark.read.parquet(wasbs_path)We now have data available in dataframe. So, we will print schema and check data.
df.printSchema()
df.show(n=2)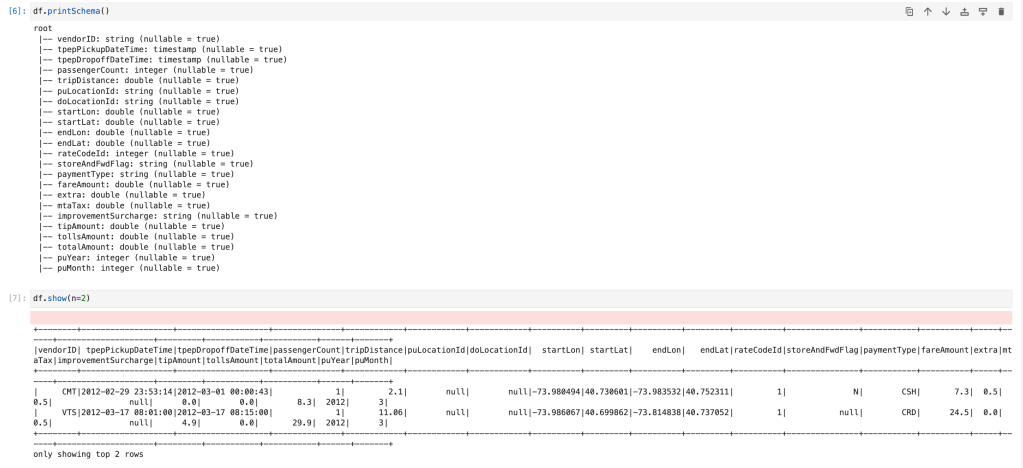
Transform data
We will create HIVE temp view. So, we can write Spark SQL and do Transformation.
df.createOrReplaceTempView('tempSource')We will select top 10 rows and create new dataframe.
newdf = spark.sql('SELECT * FROM tempSource LIMIT 10')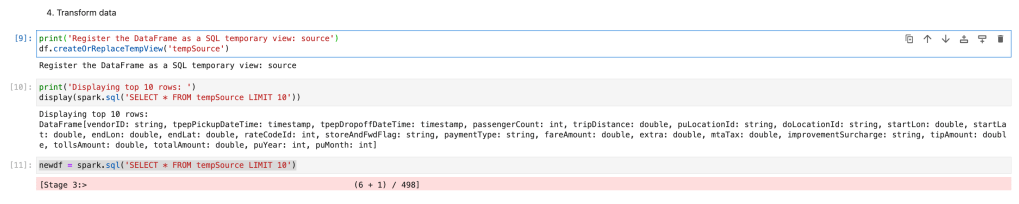
Write data into local file (Parquet | JSON)
We have data available in dataframe. Using spark. Write we can write data into different file formats.
newdf.write.format("parquet").option("compression","snappy").save("parquetdata",mode='append')
newdf.write.format("csv").option("header","true").save("csvdata",mode='append')Once this is executed, it will create folder with name “parquetdata” and “csvdata”.

Conclusion:
Once we set config of Azure blob storage or Azure Data Lake services, using spark. Read we can read files from there and using spark. Write we can write files there.