Previous blog/Context:
In an earlier blog, we discussed Spark ETL with HIVE. Please find below blog post for more details
Introduction:
In this blog, we will do Spark ETL with APIs. We will source data from API and load data into one of the below destinations. We will learn how to call APIs from Spark and create dataframe from API response. Once we have data into dataframe, we will transform and then load data into JSON and CSV format.
Today, we will perform below Spark ETL operations
- Call API and load data into dataframe
- Create temp table or view and analyze data
- Filter data and store into CSV format on file server
- Filter data and store into JSON format
First clone below GitHub repo, where we have all the required sample files and solution
https://github.com/developershomes/SparkETL/tree/main/Chapter6
If you don’t have setup for Spark instance follow earlier blog for setting up Data Engineering tools in your system. (Data Engineering suite will setup Spark, MySQL, PostgreSQL and MongoDB in your system) In that Spark instance we already have packages installed for Azure blog storage and Azure Data Lake Services.
We will use a publicly available API, for this demo we will be using the API below.
https://api.publicapis.org/entries
If you call this API from Postman/Browser, you will see response as below

Call API and load data into dataframe
First, we will start spark application and session. And after that we will call API.
# First Load all the required library and also Start Spark Session
# Load all the required library
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
#Start Spark Session
spark = SparkSession.builder.appName("chapter6").getOrCreate()
sqlContext = SparkSession(spark)
#Dont Show warning only error
spark.sparkContext.setLogLevel("ERROR")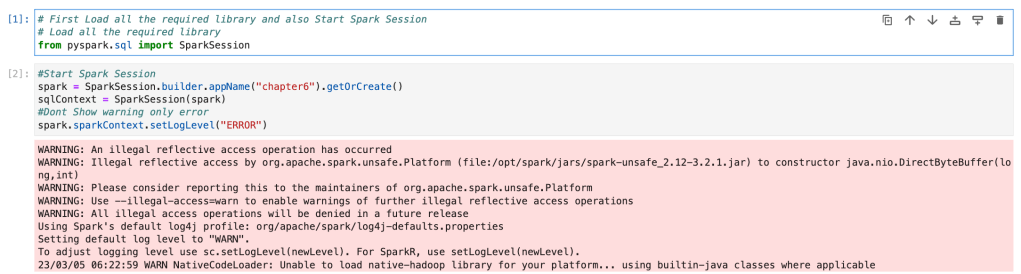
We will use the python package “request” to call API. Once we get a response from API, using “json” package, we will convert response into Json format.
#import package for calling API and formating JSON
import requests
import json
url = "https://api.publicapis.org/entries"
response = requests.request("GET", url)
# print(response.text)
jsontext = json.loads(response.text)
print(jsontext["count"])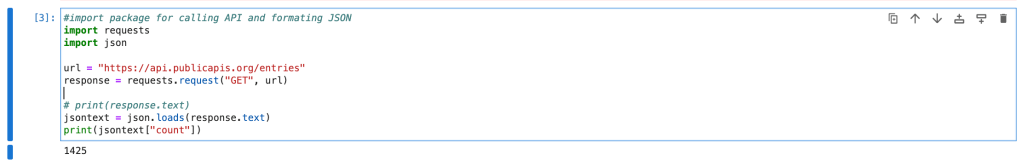
As per the Json response, we see that all the content is in entries node. So, we will get entries node into one variable. And from that list variable, we will create spark dataframe.
jsonentries = jsontext["entries"]
#Create dataframe
listdf = spark.createDataFrame(data=jsonentries)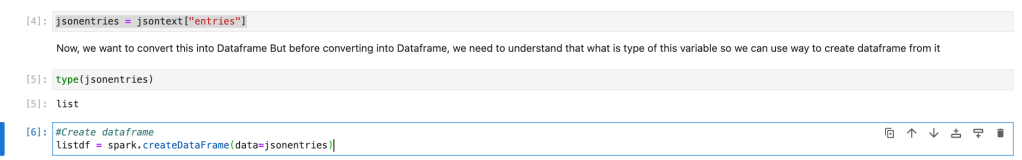
Once spark dataframe is created, we will check schema of dataframe and we will also check sample data into dataframe.
#print Schema of dataframe
listdf.printSchema()
#list first 20 open APIs
listdf.show()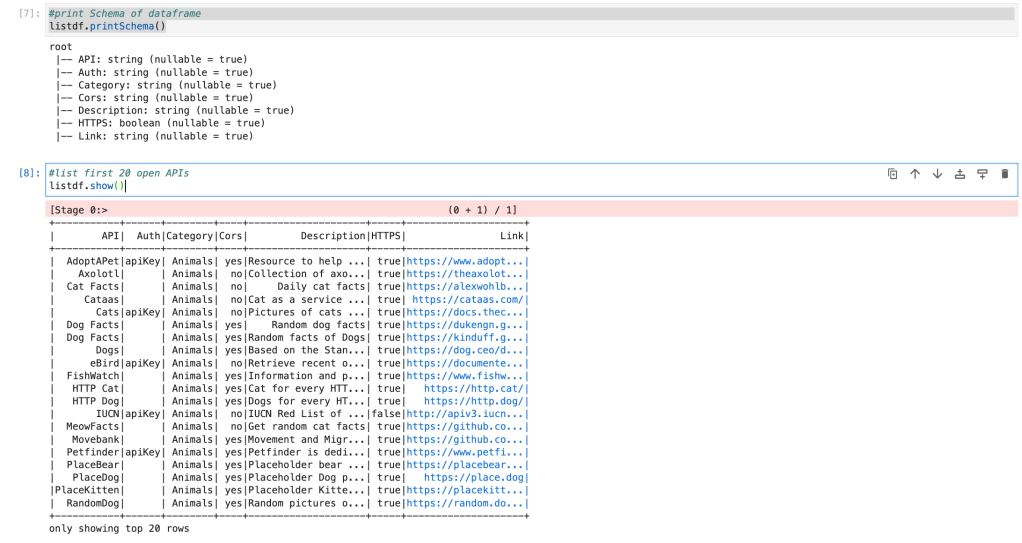
Create temp table or view and analyze data
As we discussed in earlier blog on HIVE table/view. We will create HIVE temp view from this dataframe, so that we can write Spark SQL and can do all the required transformation.
# Creating Temp Table or HIVE table
listdf.createOrReplaceTempView("tmpOpenAPI")
We will write query for getting distinct categories.
sqlContext.sql("SELECT DISTINCT(Category) FROM tmpOpenAPI").show()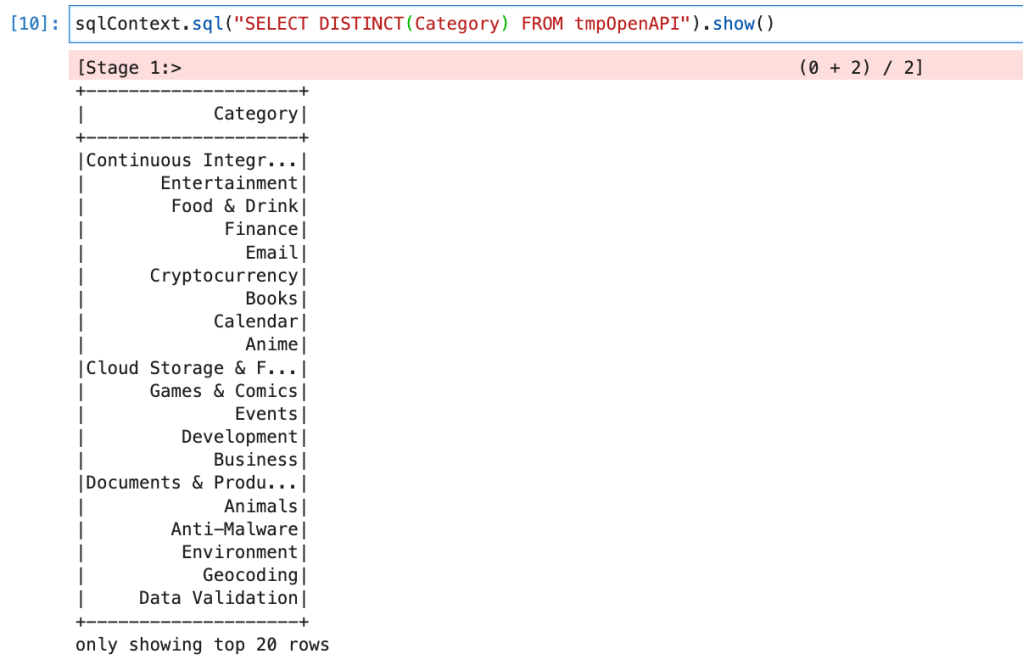
Filter data and store into CSV (& Json) format on file server
We will filter data with the category “Email” and store data into CSV and JSON format on the file server.
Query for filtering data
emaildf = sqlContext.sql("SELECT * FROM tmpOpenAPI WHERE Category = 'Email'")
Write data into CSV format
emaildf.write.format("csv").save('email.csv')
It will create a folder named “email.csv” and creates csv file inside it.
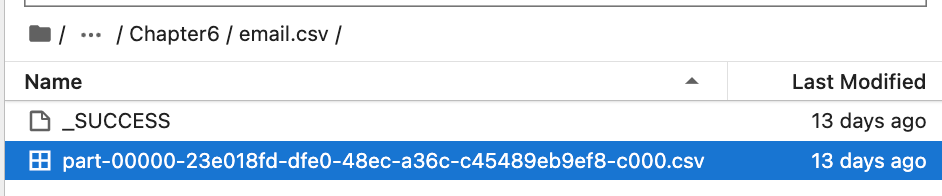
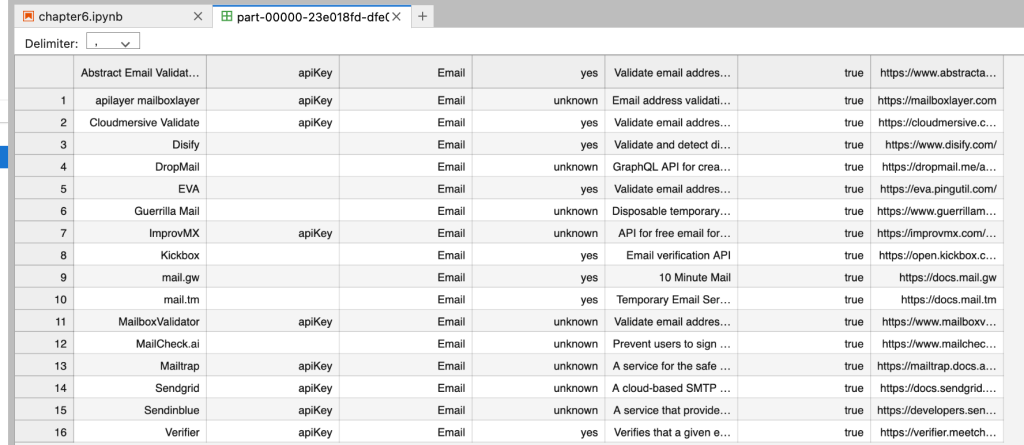
Write data into Json format.
emaildf.write.format("JSON").save('emailJSON')It will create a folder with the name “emailJSON” and will store data in Json format.

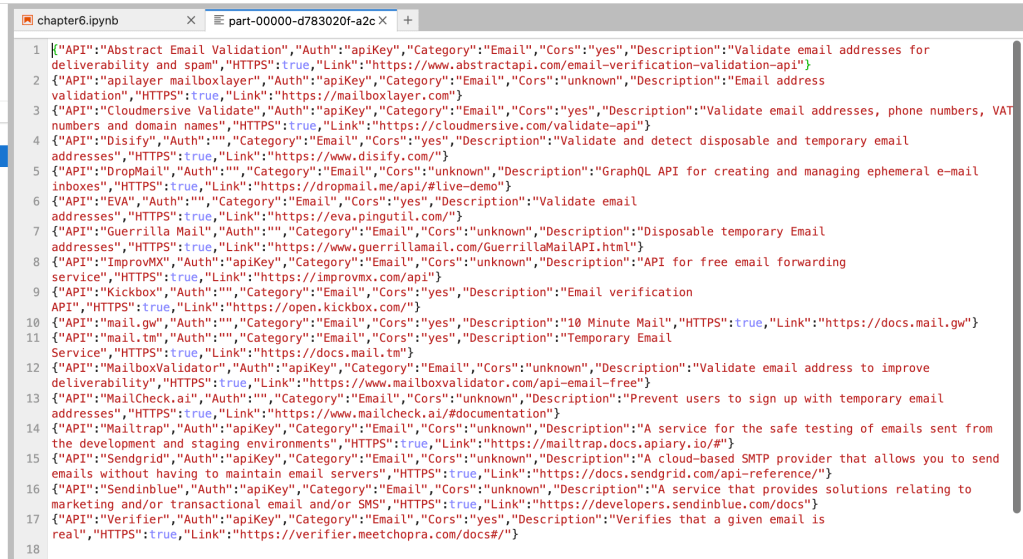
Conclusion:
Here, we learned
- How to read APIs in Spark and create spark dataframe
- How to write data into JSON format into file server (source can be anything, here we had API as source)
- How to write data into CSV format into file server (source can be anything, here we had API as source)